Silicone: The "industrial vitamin" that empowers thousands of industries
With its unique Si-O-Si main chain and organic side group structure, silicone (polysiloxane) is the only synthetic material that has the following characteristics: extreme environmental stability (temperature range from -100℃ to 350℃), physiological inertness (FDA/ISO 10993 certified) and excellent electrical insulation (dielectric strength exceeds 20 kV/mm). Relevant data show that the global market size will reach US$20.2 billion in 2024, with an annual growth rate of 6.8%.
With its excellent performance such as resistance to extreme environments, physiological inertness, and electrical insulation, silicone materials have become the core materials for improving product characteristics and enhancing industrial quality. With the explosive growth of emerging fields such as new energy vehicles, integrated circuits, and artificial intelligence, silicone is rapidly penetrating from traditional industries to high-tech fields, while leading the wave of sustainable development with its low VOC emissions and recyclability.
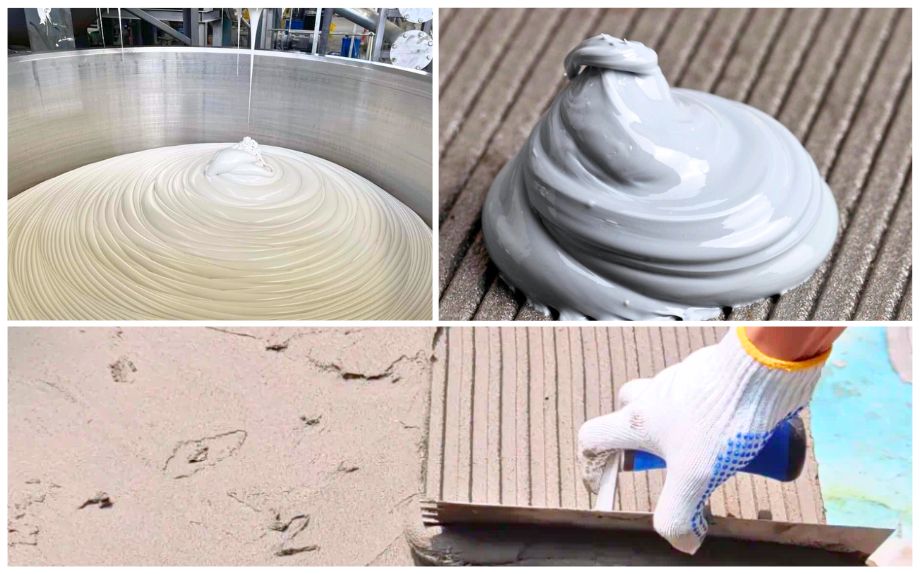
In the construction industry
Silicone adhesive is the main product. This material is based on terminal hydroxyl siloxane polymers and multifunctional siloxane crosslinkers, with auxiliary materials such as plasticizers and reinforcing agents added, and is prepared through processes such as compounding, mixing and homogenization. It has excellent elastic bonding function. It is mainly used in the fields of building (glass) curtain walls, hollow glass, DIY decoration and prefabricated buildings. In addition, silicone resin is also often used as an additive in coatings to improve the waterproof, anti-fouling and wear resistance of coatings.
Organic silicon is highly competitive in the construction market. The prosperity of the construction industry has declined in recent years, and the future consumption growth rate is expected to be only 2%. The lack of unified standards in the industry and the increased sensitivity of various links in the industrial chain to costs have led to a generally low content of siloxane, and companies are not enthusiastic enough to increase the content of siloxane in raw materials.
In the future, products with higher market appeal include modified silane sealants (MS glue) for prefabricated buildings and DIY special glue for interior decoration. The development focus of these two types of products is to improve the bonding performance to different materials and reduce the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) to meet consumers' requirements for indoor environmental quality.

Power Industry
In the power industry, the application of silicone materials covers insulators, cable accessories, flashover paints and power oil. These materials provide electrical insulation and mechanical fixation to ensure the safety and stability of transmission lines and substations.
Since the 1990s, China has achieved remarkable results in the field of composite insulators, with a market share of more than 70%. When bidding for UHV lines, the State Grid will balance the use of composite insulators, glass insulators and ceramic insulators to maintain healthy competition in the market. In the future, the market share of composite insulators will increase slowly.
At present, the application of silicone in the power industry is mainly HTV. This material has good physical and chemical properties in harsh environments, effectively resists the influence of ultraviolet rays, ozone and bad weather, and prevents flashover and ice flashover accidents. With the increase in consistency and precision requirements, the proportion of LSR in insulators is expected to gradually increase, because it has excellent fluidity and processing performance, suitable for automated production.
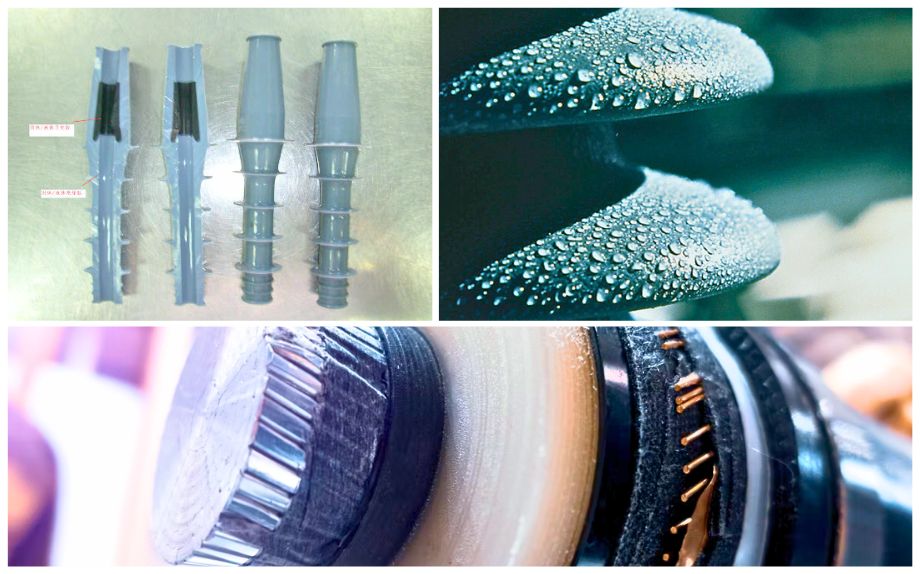
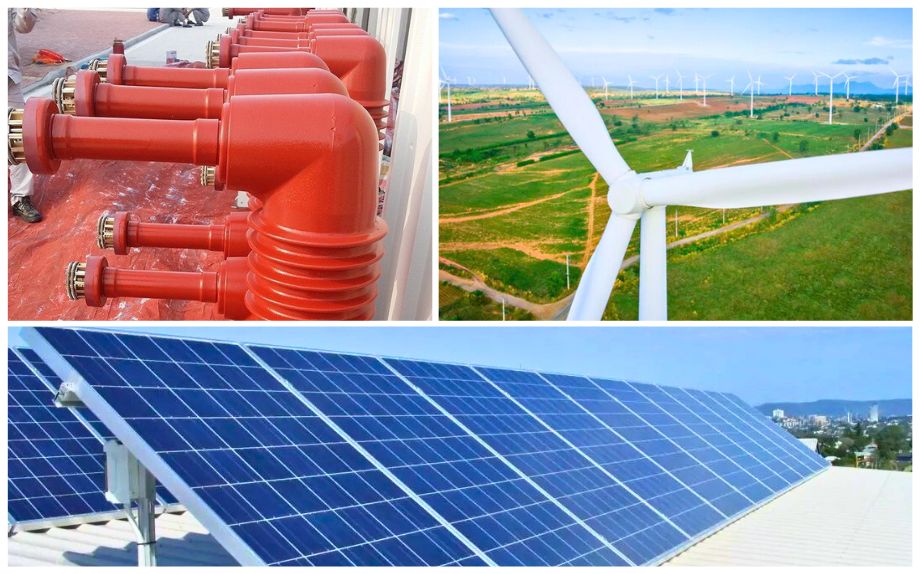
New energy industry
In the field of new energy, silicone materials are mainly used for the frame sealing of photovoltaic modules. Common products include neutral one-component silicone sealants and two-component silicone structural sealants. The bonding strength of these sealants usually exceeds 1.0MPa, which can provide long-term waterproof sealing performance, and has excellent weather resistance, ozone resistance and salt spray resistance, which is particularly suitable for the environmental requirements of photovoltaic bases. In addition, silicone-modified acrylic resins can be used for the backplane coating of photovoltaic modules, while in wind turbine blades, a small amount of silicone products are used for surface treatment and to improve the performance of epoxy resins. With the rapid development of the new energy industry, the consumption of silicone in this field will continue to grow.

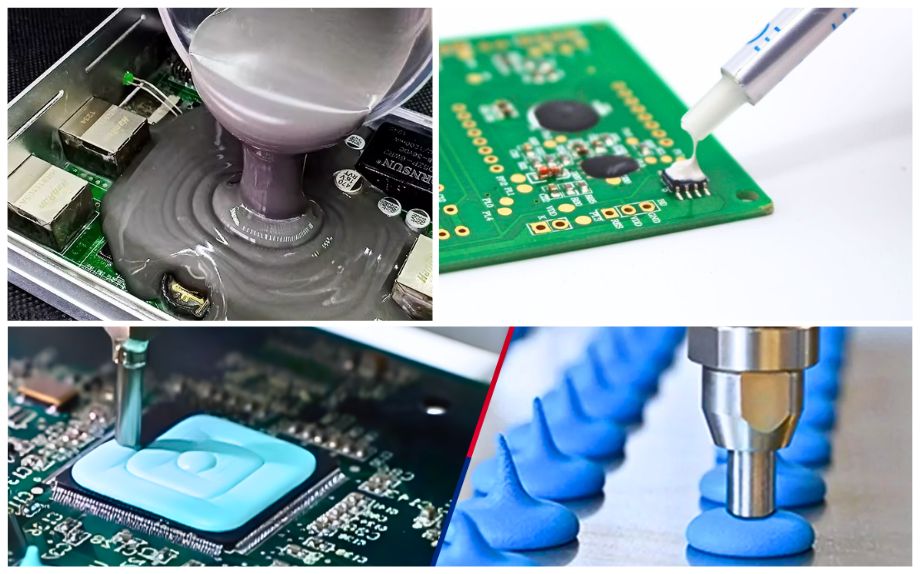
Electronics industry
In the electronics field, silicone materials have a wide range of applications, including electronic potting, thermal conductivity (such as silicone grease, silicone rubber), interface packaging, electromagnetic shielding, conformal coating and component bonding. These materials mainly provide electrical insulation, thermal conductivity, shock absorption and protection.
In actual industrial production, silicone materials are mainly used for potting of LED and IGBT (insulated gate bipolar transistor) materials. They are the second largest adhesive in the electronics and semiconductor industries, second only to epoxy resin. The electronics industry chain is complex, and the procurement of component bonding glue is usually the responsibility of component and circuit board manufacturers. In high-end fields, such as thermal interface materials for chip packaging, semiconductor design companies such as Huawei and HiSilicon have the dominant power over material selection.
With the continuous improvement of computing power, the requirements for semiconductor thermal management are also increasing, and the demand for thermal conductivity of silicone materials is growing. At the same time, with the development of flexible electronic devices and automotive electronics, the requirements for chip environmental adaptability are also increasing. Silicone adhesives that can provide better weather resistance, low temperature performance and soft shock absorption will have greater market opportunities.
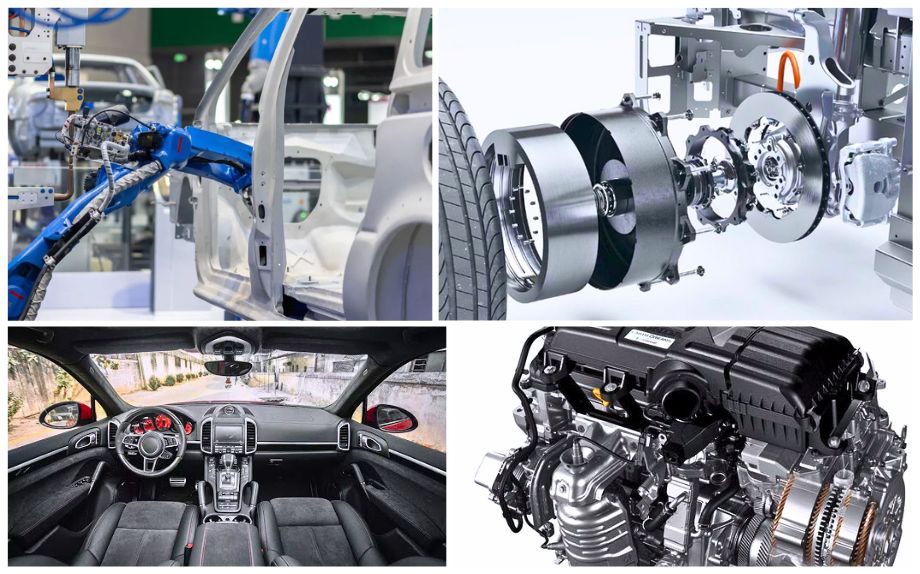
Automotive industry
In the automotive industry, silicone materials play an important role. The amount of glue used in a traditional fuel vehicle is about 2-3kg, and its applications cover engines, electronic control, shock absorption and lubrication, cooling and lighting, and interior decoration. In the field of new energy vehicles, due to its unique high and low temperature resistance, electrical insulation, waterproof and moisture-proof, and flame retardant properties, silicone products are widely used in battery packs, battery management systems, motors, electronic controls, interiors, exteriors, lights, and chassis, and the amount has increased by 3-5 times.
The application of silicone in the automotive industry includes new applications such as high-voltage cables, harness sealing, braided tube coatings, and battery protection/sealing thermal management gels. It is expected that in the next five years, the growth rate of cable harnesses and thermal conductive potting glue will be the fastest, mainly due to the increase in automotive electronic applications and the increase in thermal management needs.
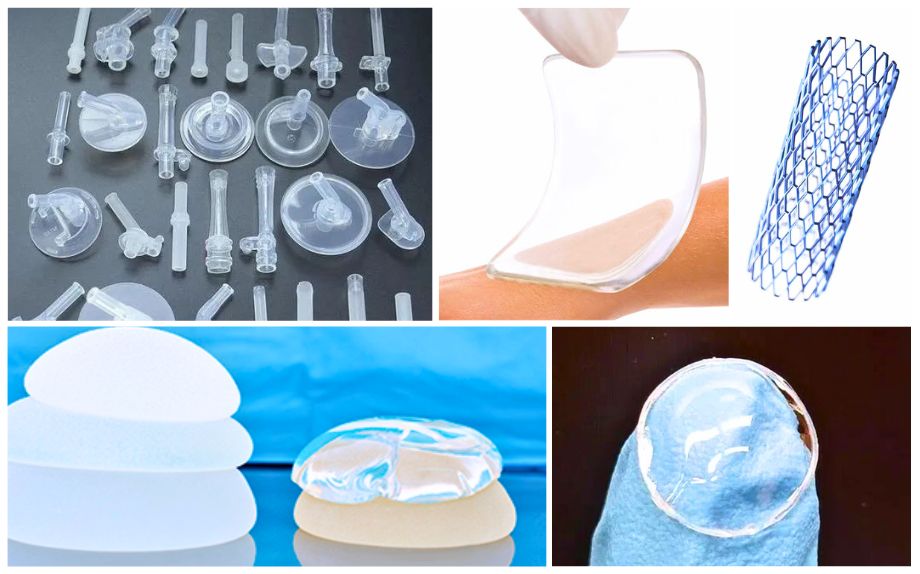
Medical and health industry
The basic structural unit of silicone is the silicon-oxygen chain link, which makes silicone materials have both the characteristics of organic matter and the functions of inorganic matter. The methyl group on the silicon atom can shield the high-energy polysiloxane main chain, thereby improving the chemical stability and biocompatibility of the material. In particular, LSR (liquid silicone rubber) products, due to their stable chemical properties, non-toxic and low sensitivity, will not cause adverse reactions when in contact with human tissues, and their soft and breathable properties make them very suitable for use in the medical and pharmaceutical industries, such as medical hoses, wound dressings, and human implant materials (such as plastic surgery, retention needles, and contact lenses).

In addition to the above applications, silicone can also be widely used in many fields such as home decoration (such as silicone leather), kitchen appliances (such as high-temperature sealing rings), maternal and child products (such as pacifiers), and industrial additives (such as defoamers and release agents). It is expected that the market growth rate of the silicone industry will be higher than the GDP growth rate in the next few years. By 2030, the global demand for silicone products will reach about 6.8 million tons, with an average annual growth rate of 8.5%. The power industry is expected to surpass the construction industry and become the main consumer of silicone.
Although silicone materials face challenges from competing materials, such as the high prices of new chemical materials such as polyurethane, which limits the use of silicone as the main material. At the same time, as a common adhesive material, its mechanical properties are relatively poor. Scientific research institutions are exploring methods to improve the mechanical properties of silicone materials, including cross-linking modification, surface modification, copolymerization modification and fiber reinforcement.
The main advantages of silicone materials are thermal conductivity, weather resistance, biocompatibility and skin affinity. The future development direction should focus on these application links. With the rise of new technology fields such as AI, new applications of silicone materials will continue to emerge. The development of Chinese silicone materials should shift from following the Western market to actively looking for and incubating new application scenarios.
