An Introduction to Silicone
Release Time: 2022-10-21 14:05:15
An Introduction to Silicone
In our last blog we have introduced some basic chemical characteristics & applications of silicone and its broadly extensions- silicone oils & LSR silicone rubbers.
Today, we will introduce more about the nature and the history of silicone element rather than just one specific silicone product which is developed from it.

(silicone oils and silicone rubbers-liquid form)
What is Silicone?
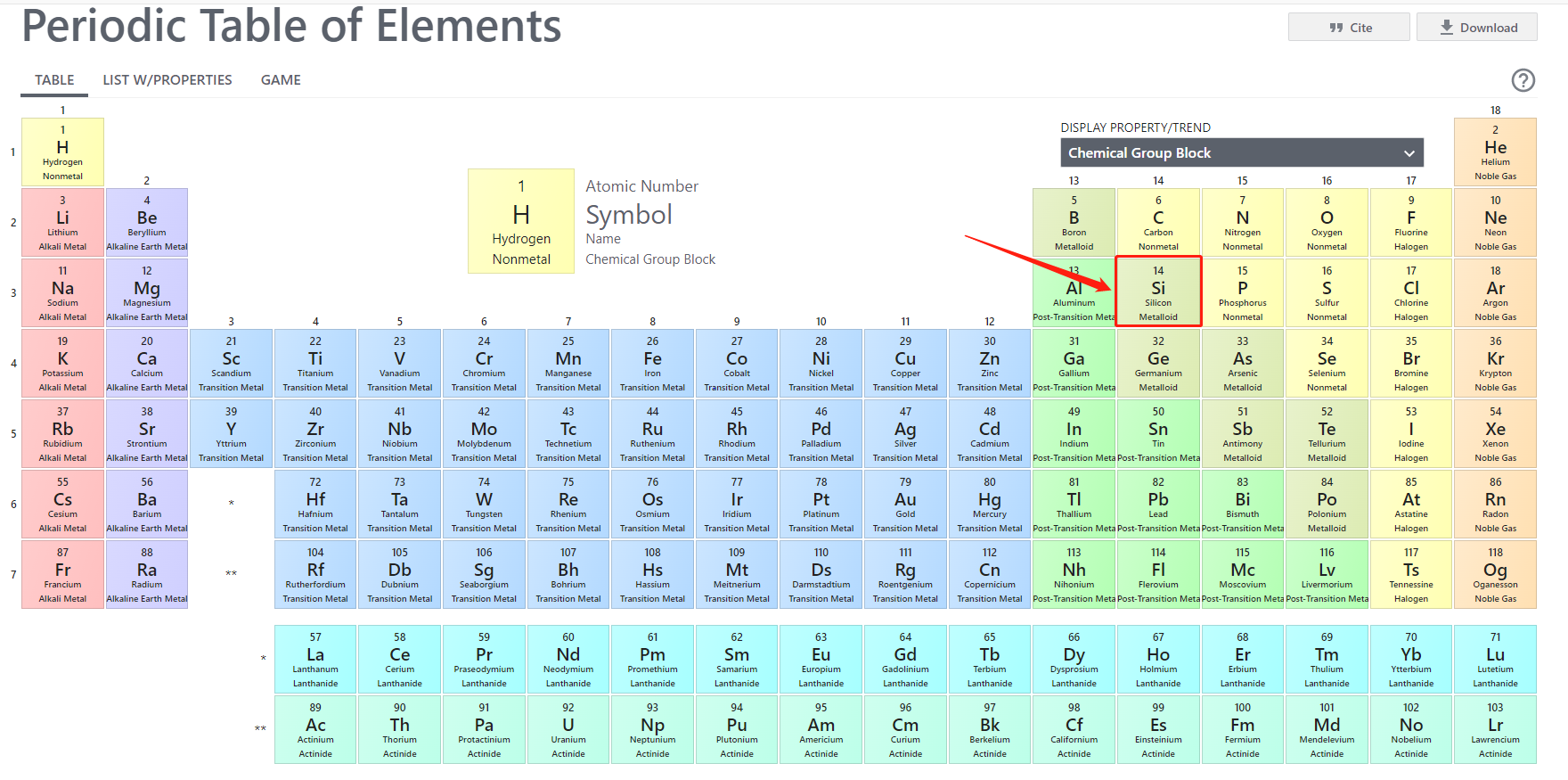
Silicone is a chemical element which could be seen in everyday life easily; the name is originated from Latin word “silex”. Its symbol is Si and its atomic number is 14. The amount of storage of silicone is 25.7% in the earth curst and which is only lower than oxygen (which is 49.4%). It is thus the second richest element.
Silicone has both of physical & chemical characteristics between metalloids’ and non-metals’. It is because its ranking in the periodic table of the elements- it is in the same row as carbon and germanium and the position is just between these two elements (shown as the picture below). Sometimes silicone is considered as a semi-metalloid.