The new material revolution of humanoid robots
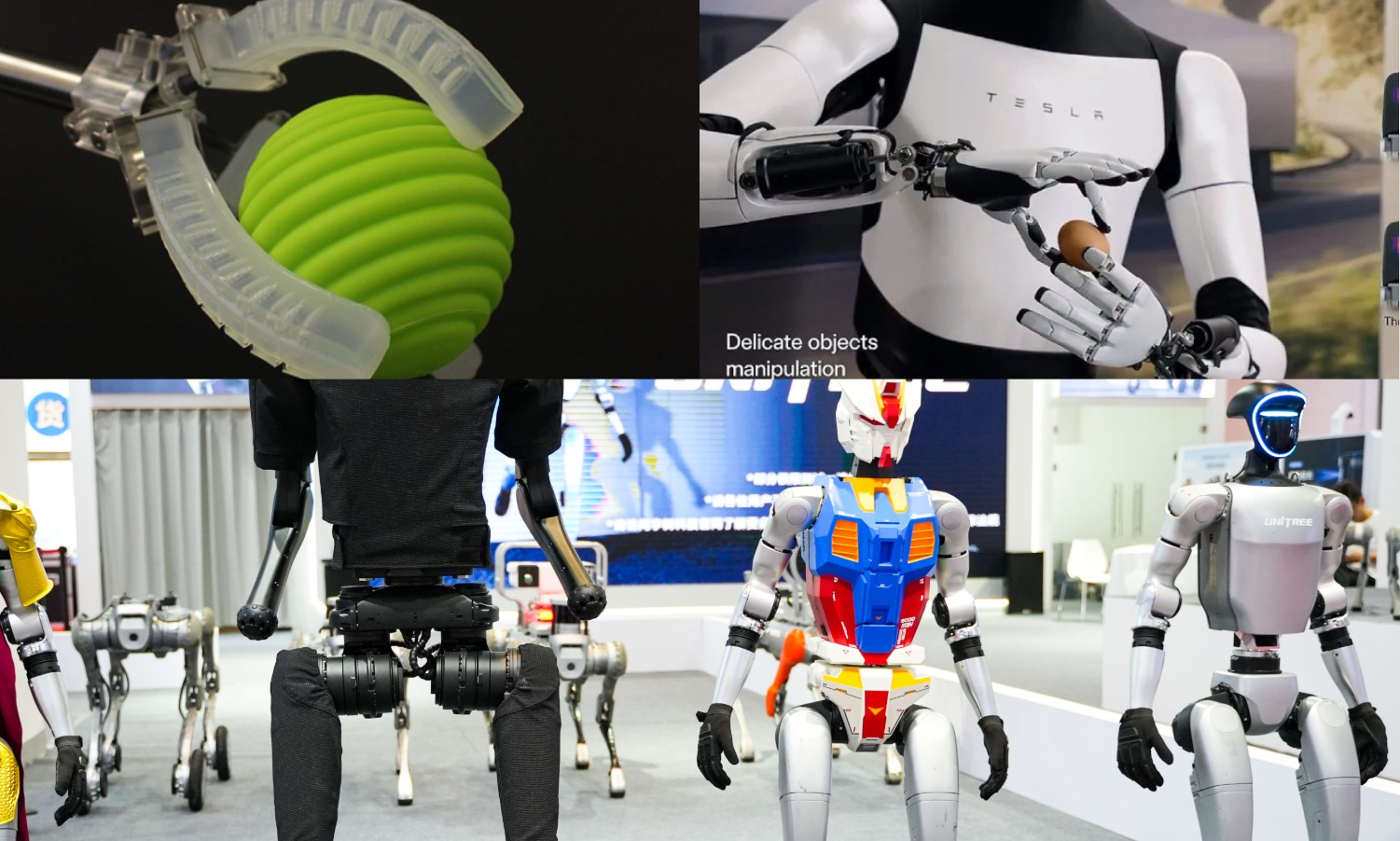

In recent years, the humanoid robot track has experienced explosive growth. The iteration of products such as Tesla Optimus, Boston Dynamics Atlas, and UBTECH Walker X not only makes the flexibility of the "steel body" close to that of humans, but also drives revolutionary breakthroughs in upstream new materials. From flexible joints to bionic skin, from energy systems to intelligent sensors, key materials such as silicone, liquid metal, and carbon fiber are standing on the cusp of the industry and have become the focus of global technology giants and capital.
In the 2025 Chinese Spring Festival Gala, 16 Unitree H1 "Fuxi" robots from Unitree Technology starred in the creative dance program "Yang BOT". It showcases China's cutting-edge robot technology. H1 is the world's first full-size electric-driven humanoid robot that can complete a flip in place. It is equipped with AI-driven full-body motion control technology, high-precision 3D laser SLAM autonomous positioning and navigation, multi-agent collaborative planning, advanced networking solutions, and full-body AI motion control.

Humanoid robots have requirements for materials such as corrosion resistance, heat resistance, insulation, lightweight, and environmental protection. Limb skeletons are the basic framework that supports humanoid robots to perform various actions. Its application scenarios include shell materials, spine, upper arms, lower arms, thighs, lower legs and other structural parts. Commonly used materials include steel, aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy, carbon fiber, polymer materials, etc.
1. Humanoid robots trigger the demand for new materials
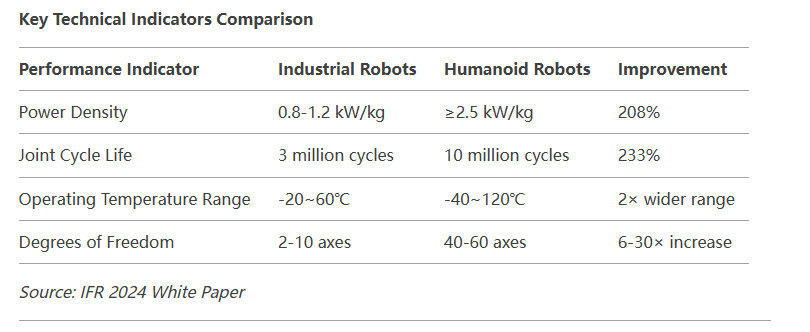
The stringent requirements of humanoid robots for materials far exceed those of traditional industrial robots:
Motion system: high strength, lightweight, and fatigue resistance must be met at the same time (such as the cycle life of joint materials must exceed 10 million times)
Perception system: materials are required to have conductivity, ductility, and environmental adaptability (40℃~120℃)
Interactive interface: Bionic materials must achieve skin-like touch, self-repair, and even emotional feedback
According to Shengbangfan's forecast, by 2035, the humanoid robot market will reach US$154 billion, with core material costs accounting for more than 60%, giving birth to a new material market worth hundreds of billions of yuan. At present, the main materials are silicone, polyamide, polyetheretherketone, carbon fiber reinforced composite materials, liquid crystal polymer (LCP), polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), and liquid metal.

2. Analysis of main materials
1. Silicone
Silicone is an organosilicon compound, which refers to a compound containing SiC bonds and at least one organic group directly connected to the silicon atom. It has the characteristics of softness and skin-friendly, high and low temperature resistance, radiation resistance, non-toxicity and tastelessness, as well as good biocompatibility and environmental stability. It has always played an important role in the fields of automobiles, aircraft, military technology, and electronic equipment, and has promising application prospects in the fields of flexible electronic devices and flexible robots.
The hands of soft robots usually need to be able to perform delicate operations while interacting safely with humans. The flexibility, transparency and biocompatibility of silicone can meet the material use requirements. The soft robot hand developed by Soft Robotics is made of silicone and can be used in industries such as packaging, assembly and food processing.
2. Polyamide (PA)
Poppy, a robot designed by Ensta ParisTech and Flowers Lab from France, has all its parts 3D printed except for the motor and electronic circuits, using the selective sintering (SLS) process, and the material is polyamide (PA).
3. PEEK (polyether ether ketone)
In early 2024, Tesla demonstrated the OptimusGen2 second-generation humanoid robot, which reduced weight by 10 kg without sacrificing performance and increased walking speed by 30%, relying on a lightweight material - PEEK material. PEEK is one of the important raw materials for the production of humanoid robots.
4. Carbon fiber reinforced composites
Carbon fiber composites, also known as "CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics)", are composite materials made by curing carbon fibers with resin (mainly epoxy resin). As a light and strong, light and hard material, it is widely used in sports products, industrial products, aircraft and automobiles.
Advantages: Density 1.6g/cm³, strength 79 times that of steel
Innovation: Toray T1100G+epoxy resin system, reducing weight by 30% while improving torsional rigidity
Application: Robot skeleton, lightweight robotic arm
5. Liquid crystal polymer (LCP)
Ordinary industrial robots have joints between 210 axes, while the number of joints in humanoid robots is expected to be more than 40 (Tesla Optimus 40), and each joint requires a servo motor, so the servo motor is one of the main core components of humanoid robots. Special engineering plastics, especially LCP materials, are widely used in electronic components such as robot servo motor connectors. LCP (Liquid Crystal Polymer), also known as liquid crystal polymer, has excellent properties such as good fluidity, good dimensional stability, high temperature resistance, and high-frequency dielectric stability. It is suitable for precision components and is one of the best material choices for micro motors and high-frequency signal connectors.
6. Liquid metal
The Chinese Academy of Sciences team developed a GaInSnZn amorphous alloy with a yield strength of 520MPa at room temperature (3 times that of traditional liquid metal), which was successfully applied to the knee joint of the Yushu H1 robot (Nature Materials 2024.01)
Apple has obtained a patent for liquid metal self-healing circuits (US2024367821A1), which can achieve automatic healing of microcracks.
The evolution of humanoid robots is essentially a breakthrough in materials science. From the PEEK spine of Tesla Optimus-Gen2 to the liquid metal joints of Yushu H1, from the carbon fiber legs of Boston Dynamics Atlas to Apple's self-healing circuits, this demand-driven material revolution is reshaping the industry at an exponential rate. According to McKinsey's forecast, by 2030, there will be 23 new materials developed specifically for humanoid robots in the world that will be commercialized and mass-produced, among which the market size of bionic self-healing materials and intelligent response composite materials will exceed US$80 billion. China has shown unique advantages in this competition - the Chinese Academy of Sciences' liquid metal technology has made the leap from laboratory to production line, while BYD, CATL and other giants' layout in the field of special engineering plastics is accelerating the process of domestic substitution. In the next five years, with the maturity of multi-material heterogeneous integration technology and AI-driven material design platform, humanoid robots may break through the "mechanical" boundary, truly realize the anthropomorphic transformation of "flesh and blood", and open a new era of intelligent manufacturing.
